
You may ask why I need such a big disk space, most of the space is devoted to computer backups, which I only keep locally as opposed to sending to a cloud backup – it is too big and changes daily. All together gives me about 70 TB, which is a 35TB in a mirror configuration. The smallest pair of disks are 3TB, then a group of 4TB, 6TB, 10TB and lately I added two 12TB disks. It has 12 hard disks, in a mirror configuration. I have a Storage Spaces pool that got larger over the years. My solution for file-insurance: have local redundant storage as well as a cloud-based backup.
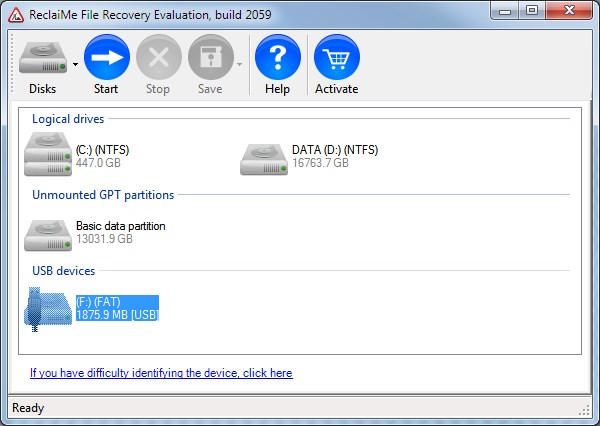
Hard drives are fragile the internet bandwidth is still not fast enough to back up large amounts of data in a timely manner. If you are in such a situation, I’m pretty sure that you’ll read every word, I read everything I can when I search for a cure to a problem. This is going to be a long “Diary” like a blog post that describes over a month of a fight to bring back a 35TB (70 TB physical disk space) logical disk to life.

Many PowerShell commands, as well as administrative user interface, let you manage Storage Pools and Virtual Disks that you allocate from them. If you have a single disk failure, you are safe, in some configuration storage spaces can protect a multiple disk failure, but it requires many hard disks. Storage Spaces lets you add more disks as well as remove old or broken disks. You can have a simple spanning configuration (RAID 0), a mirror configuration (RAID 1) or a parity configuration (RAID 5). This is a software RAID system that lets you create a Storage Pool out of many physical hard disks. You may use this technology when having a large disk space that can dynamically grow, by stripping many physical hard disks. However, Microsoft has brought this technology to Windows 10 and Windows Server Essentials – what used to be the Small Business Server. Storage Spaces is a technology that is mainly used by large file servers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
